Extended-deep Q-network: A functional reinforcement learning-based energy management strategy for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles
Abstract
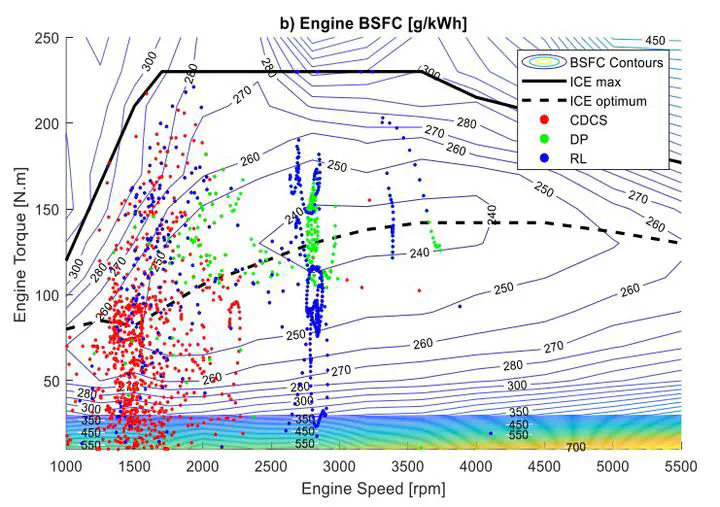
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles offer a promising solution for the increasing CO2 emission problem. However, the improved economy strongly depends on the energy management strategy. Traditional rule-based strategies are no more practical considering the increasing complexity in control objectives. In this study, an adaptive online Reinforcement Learning (RL) agent is developed, which learned an energy management strategy with a near-optimal performance. A novel hybrid approach is proposed to integrate the agent into the existing rule-based hybrid control unit architecture with a limited operation domain for more practicality and suitability to series-production control systems. Dynamic Programming (DP) and rule-based strategy are used to benchmark the developed RL agent performance. The objective is to minimize the vehicle’s total fuel consumption and the frequent engine on/off switching to improve driver comfort and vehicle drivability. Several RL-based algorithms have been experimented and as a result, an Extended-Deep Q-Network (E-DQN) agent is proposed by this paper, trained on one cycle, and deployed on two other cycles with different onboard energy levels to evaluate the performance. The paper findings showed that E-DQN outperformed the rule-based strategy achieving up to 10.46% improvement in fuel economy closer to the DP performance alongside providing adequate compliance with the vehicle drivability and driver comfort objectives.